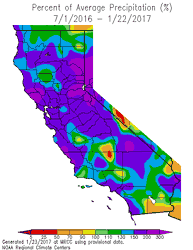
California Percent of Normal Precipitation (WRCC)
July 1, 2016 to January 22, 2017
Update on February 2, 2017. Downtown Los Angeles has ended January 2017 with 8.38 inches of rain. This is 269% of the normal January rainfall total of 3.12 inches. The preliminary Rain Year precipitation total for Downtown Los Angeles for July 1 through January 31, 2017 is 14.33 inches, which is 193% of the normal amount of 7.44 inches. Here is an updated California Percent of Normal Precipitation map from the Western Regional Climate Center for July 1, 2016 to January 31, 2017.
On the heels of a wet December, a series of Pacific storms have resulted in the wettest start to the Rain Year (July 1 - June 30) and Water Year (October 1 to September 30) since the very wet year of 2004-2005.
The six day period from January 18-23 was particularly wet, with three storms producing a total of 5.53 inches of rain at Downtown Los Angeles (USC). Here are some preliminary 7-day precipitation totals from around the area from the Ventura County Watershed Protection District.
The last system of the series, which brought very heavy precipitation to the area on Sunday, was associated with a well-defined atmospheric river. Precipitation totals in the Los Angeles area for the storm generally ranged from about 2 to 5 inches. According to the NWS, new rainfall records for January 23 were set at Los Angeles Airport (2.94 inches), Camarillo (2.74 inches) and Long Beach Airport (3.97 inches). The rainfall at Long Beach Airport was the most ever recorded in a day at that location. Here are some precipitation totals from around the area compiled by the NWS Los Angeles/Oxnard and NWS San Diego.
As of yesterday Downtown Los Angeles (USC) has recorded 14.33 inches of rain for the Rain Year. This is 217% of the normal amount of 6.65 inches for the date, and 97% of the normal amount of rainfall for an entire year. Assuming we don't get any more rain this January, the 8.38 inches recorded will work out to 269% of the normal amount for the month.
The California Cooperative Snow Surveys Snow Water Equivalents report for today puts the snowpack for the date at an average 197% of normal. That's two times the normal amount.
A little precipitation has crept back into the GFS, GEFS and ECMWF forecasts for the Los Angeles area the first week of February. We'll see!
More information about Southern California weather and climate can be found using our WEATHER LINKS page.